#Meditation is Good for Our (#Aging) #Brains
In case you were wondering, and I was, why so many of my Buddhist friends and fellow meditators are mentally so healthy and over the ages of 65, 70, 75, I decided to “look it up” and see if my suspicions were correct. They are.
If we’re lucky enough not to have anything else kill us or ruin our brains, meditation DOES have a measurably profound, positive impact on our mental and physical health, particularly on maintaining cognitive functionality into our senior years.

And, it’s not just those in my experience whose brains are doing great: meditators everywhere (if we could study us all) most likely have brains that are younger, more pliable, and less prone to diseases of aging, even as the calendars march us onward. This is a club you want to join!
No need to ditch your current religion, spirituality, atheism or anything: just learn to meditate and do it regularly!
“A [2016] study suggested that taking time from your busy schedule to meditate can actually help preserve your mind and slow Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Learn more about how meditation can slow Alzheimer’s.” https://www.jeffersonhealth.org/your-health/living-well/yes-meditating-can-reverse-cognitive-decline-heres-how#:~:text=Yes%2C%20Meditating%20Can%20Reverse%20Cognitive,Here’s%20How%20%7C%20Jefferson%20Health
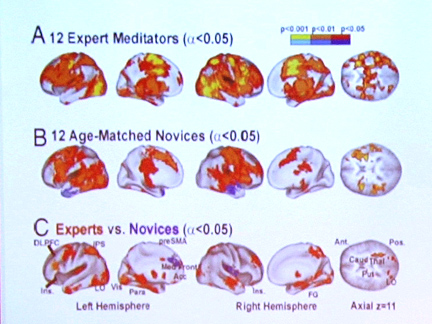
Meditation has been shown to slow the typical aging effects on our brains very specifically. This longitudinal individual study, quoted and linked, below, makes me smile, since I know this Rinpoche (an honorific Tibetan term meaning “precious teacher”).
“Using MRI and a machine learning framework which estimates ‘brain-age’ from brain imaging, [neuroscientist, Richard] Davidson and lead scientist, Nagesh Adluru, studied the mind of Tibetan Buddhist meditation master, [His Eminence] Yongey Mingyur Rinpoche, over the course of 18 years….
“Rinpoche was first scanned in 2002 at the age of 27. At the time, he had already completed nine years of meditation retreats. He was scanned again at the respective ages of 30, 32 and 41 years old.
“The last time he was scanned, he had just returned from a four-and-a-half-year wandering retreat, and his brain was calculated to be 33-years-old, eight years younger than his biological age.
“The researchers compared Rinpoche’s aging brain to a control group and his appeared to age much slower than the general focus group.”
https://www.cnn.com/2020/03/20/health/meditation-slows-brain-age-trnd-wellness/index.html#:~:text=A%20recently%20pubished%2018%2Dyear,compared%20to%20a%20control%20group

So, how long does it take and how much meditation do we need to do to gain positive effects? Read on and check out the longer articles in each link.
How long you need to meditate to see results for your body and brain
“…[M]editation can affect the brain and body in myriad ways, from reducing the risk for chronic diseases to lowering the risk for anxiety and depression….
“Research shows meditation reduces stress, anxiety, and depression symptoms. A 2016 study found that longer-term meditation practice was associated with structural changes of the ‘white matter’ in the brain, which is responsible for ‘relaying sensory information’ and can explain why meditation helps people stay in the present moment and may help combat age-related cognitive decline.
“A more dated study found an increase in gray matter in the brain’s hippocampus, the areas associated with memory, emotional regulation, self-processing, and perspective taking, with regular meditation.
“‘The practice also enhances attention, and increases the ability to cultivate awareness around emotions so they don’t bubble up later,’ Gonzalez says….
“Studies point to 8-weeks of meditation practice to see results. One study found improvements to memory, emotional regulation, and mood with 8 weeks of 13 minutes of meditation a day. But there isn’t a magic number.
“Gonzalez, who has trained over numerous leaders in the practice, says: ‘as little as 10 minutes can make a difference. What matters most is dedicating yourself to the technique (that means not checking work notifications in the middle of a practice).'”
| How long you need to meditate to see results for your body and brain? It can take as little as 10 minutes a day to rewire the brain. |
Neurologists, neuroscientists, gerontologists, psychiatrists and others are VERY interested in these results! More, below.
“‘Mental training that targets stress and attention regulation has the potential to improve both cognitive and emotional aspects of ageing,’ researcher [Dr. Chetelat] says….
“Dr. Chetelat said: ‘Strategies to prevent dementia are urgently needed. Mental training that targets stress and attention regulation has the potential to improve both cognitive and emotional aspects of ageing.
“’Previous studies have shown mindfulness meditation improves cognition, specifically in older adults across multiple domains including attention, executive functions and self-awareness or meta-cognition.
“’Mindfulness meditation can also reduce stress, anxiety and depression – including in older adults.’…
”Dr. Chetelat said: ‘Meditation appears to be a promising approach to preserve brain structure and function as well as cognition and thus to reduce dementia risk by directly targeting psycho-affective factors.’”
“The study is in the journal JAMA Neurology.”
https://www.independent.co.uk/news/health/meditation-dementia-causes-mindfulness-study-b2200022.html
You can learn basic meditation from an app, a book, or a friend.
Advanced or more complicated techniques require a teacher or a class/workshop, but these are not necessary to acquire benefits listed above.
Really. Get to it, NOW! #MEDITATEDAILY!












You must be logged in to post a comment.